
Laravel is a highly regarded PHP framework used for web application development. It has gained significant popularity in the industry mainly because of its features, such as its simplicity, elegance, and robustness.
As per Builtwith, 1,729,522 have used Laravel technology, and there are 702,811 live websites worldwide. Regarding India, 20,002 websites currently use Laravel in India. As a result, the demand for talented Laravel developers is continuously increasing and is projected to rise further.
If you have to appear for an interview for a Laravel developer position, you've come to the right place. Here, we provide a comprehensive list of Laravel interview questions and answers that would help you prepare for your next interview. By familiarizing yourself with these questions, you can enhance your knowledge and confidence and gain a competitive edge in the job market. So, let's dive in and excel in your Laravel career journey!
| Quick Facts About Laravel | |
|---|---|
| What is the latest version of Laravel? | 10.0, released on February 14th, 2023. |
| When was Laravel first released? | June 2011. |
| Laravel is Created By | Taylor Otwell |
| What language does Laravel use? | PHP |
| Which is the best IDE for Laravel? | Netbeans, PhpStorm, Atom, Sublime Text |
Laravel Developer Interview Questions (2024)
- What is Laravel and how does it differ from other PHP frameworks?
- What are the key features of Laravel?
- What is the importance of Composer in Laravel?
- What are Service Providers and how do they work in Laravel?
- What is the purpose of Facades in Laravel?
- What is the difference between Eloquent and Query Builder in Laravel?
- What is a Middleware in Laravel and how is it used?
- What is the purpose of Artisan in Laravel and how is it used?
- What is the difference between a Repository and a Service in Laravel?
- How do you implement caching in Laravel?
- How do you handle errors and exceptions in Laravel?
- What is a Service Container in Laravel and how is it used?
- How do you implement Authentication and Authorization in Laravel?
- What are Laravel Contracts and how are they used?
- How do you create and use Events and Listeners in Laravel?
- What is the purpose of Queues in Laravel and how are they implemented?
- How do you implement Localization in Laravel?
- What is a Trait in Laravel and how is it used?
- What is the difference between CSRF and XSS attacks in Laravel?
- How do you optimize the performance of a Laravel application?
Most Frequently Asked Laravel Interview Questions
Here in this article, we will be listing frequently asked Laravel Interview Questions and Answers with the belief that they will be helpful for you to gain higher marks. Also, to let you know that this article has been written under the guidance of industry professionals and covered all the current competencies.
It is a free, powerful and open-source PHP framework that follows the model–view–controller design pattern. It is a very popular framework which is developed in PHP, and that reduces the cost of development and improves code quality. It is produced by Taylor Otwell. The first version of laravel is released on 9 June 2011.
Features of Laravel
- Eloquent ORM
- Query builder available
- Reverse routing
- Restful controllers
- Migrations
- Database Seeding
- Automatic pagination
- Unit testing
- Homestead
The latest version of Laravel is 7.0. It released on 3rd March 2020.
Laravel installation steps:-
- Download composer from https://getcomposer.org/download (if you don’t have a composer on your system)
- Open cmd
- Goto your htdocs folder.
- C:\xampp\htdocs>composer create-project laravel/laravel projectname
OR
If you install some particular version, then you can use
composer create-project laravel/laravel project name "5.6"
If you did not mention any particular version, then it will install with the latest version.
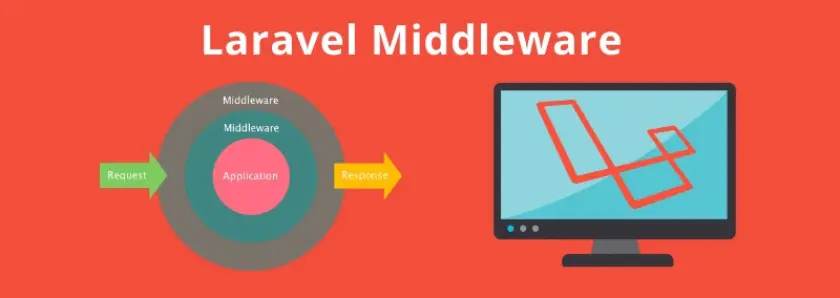
Middleware in laravel works as a platform among the request and the response. It provides the mechanism for investigating the HTTP requests which are entering into your application. For instance, middleware in laravel ensures that the user of your particular application is authenticated. If they found that the user is not authenticated, it will redirect the user to the main login page of the application.
Example: If a user is not authenticated and it is trying to access the dashboard then, the middleware will redirect that user to the login page.
These are the most important concepts used in Laravel
- Blade Templating
- Routing
- Eloquent ORM
- Middleware
- Artisan(Command-Line Interface)
- Security
- In built Packages
- Caching
- Service Providers
- Facades
- Service Container
Database migration is like the version control of the database, which allows the team to modify and share the database schema of the application. Database migrations are paired with the schema builder of Laravel which is used to build the database schema of the application.
It is a type of version control for our database. It is allowing us to modify and share the application's database schema easily.
A migration file contains two methods up() and down().
up() is used to add new tables, columns, or indexes database, and the down() is used to reverse the operations performed by the up method.
You can generate a migration & its file with the help of make:migration
Syntax : php artisan make:migration blog
A current_date_blog.php file will be created in database/migrations.
Service providers are the fundamentals of bootstrapping laravel applications. All the core services of Laravel are bootstrapped through service providers.
These powerful tools are used by developers to manage class dependencies and perform dependency injection. To create a service provider, we have to use the below-mentioned artisan command.
You can use php artisan make: provider ClientsServiceProvider artisan command to generate a service provider :
It has the below listed functions in its file.
- register function
- boot function
Lumen is a newly introduced micro PHP framework which is a faster, smaller and leaner version of a full web application framework. It is introduced by Taylor Otwell, the creator of Laravel. It uses the same components as Laravel, but especially for microservices.
It has a simple installer like Laravel. You have to use this command to install lumen.
composer global require "laravel/lumen-installer=~1.0"
We can add that particular URL or Route in $except variable. It is present in the app\Http\Middleware\VerifyCsrfToken.php file.
class VerifyCsrfToken extends BaseVerifier {
protected $except = [
'Pass here your URL',
];
}
Laravel uses "Blade Template Engine". It is a straightforward and powerful templating engine that is provided with Laravel.
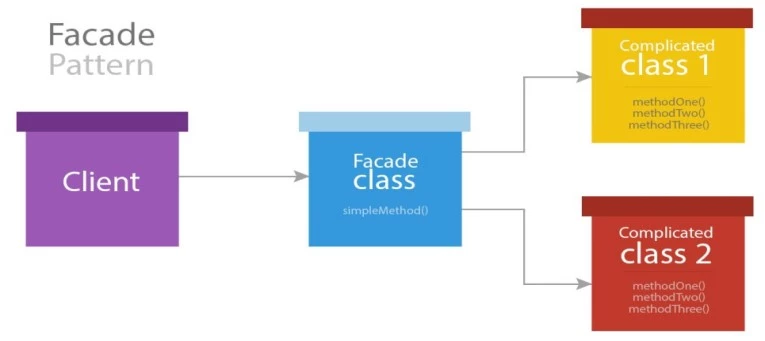
The facade gives the “static” interface to all the classes available in the service container of the application. Laravel comes along with many interfaces that provide the access to almost all the features of Laravel.
All the facades are defined in the namespace Illuminate\Support\Facades for easy accessibility and usability.
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
Route::get('/cache', function () {
return Cache::get('PutkeyNameHere');
});
We can create a helper file using Composer. Steps are given below:-
- Please create a app/helpers.php file that is in app folder.
- Add
"files": [
"app/helpers.php"
]
in "autoload" variable. - Now update your composer.json with composer dump-autoload or composer update
It acts as a middleman between a request and a response. Middleware is a type of filtering mechanism used in Laravel application.
- We can create middleware with
php artisan make:middleware UsersMiddleware - Here "UsersMiddleware" is the name of Middleware. After this command, a "UsersMiddleware.php" file is created in app/Http/Middleware directory.
- After that we have to register that middleware in kernel.php (available in app/Http directory) file in "$routeMiddleware" variable.
'Users' => \App\Http\Middleware\UsersMiddleware::class, - Now we can call "Users" middleware where we need it like controller or route file.
- We can use it in a controller file like this.
public function __construct() {
$this->middleware('Users');
} - In route file we can use like this.
Route::group(['middleware' => 'Users'], function () {
Route::get('/', 'HomeController@index');
});
Artisan is a type of the "command line interface" using in Laravel. It provides lots of helpful commands for you while developing your application. We can run these command according to our need.
Laravel supports various artisan commands like
- php artisan list;
- php artisan –version
- php artisan down;
- php artisan help;
- php artisan up;
- php artisan make:controller;
- php artisan make:mail;
- php artisan make:model;
- php artisan make:migration;
- php artisan make:middleware;
- php artisan make:auth;
- php artisan make:provider etc.;
A laravel service container is one of the most powerful tools that have been used to manage dependencies over the class and perform dependency injections.
Advantages of Service Container
- Freedom to manage class dependencies on object creation.
- Service contain as Registry.
- Ability to bind interfaces to concrete classes.
Laravel provides a powerful and clean API over the SwiftMailer library with drivers for Mailgun, SMTP, Amazon SES, SparkPost, and sending an email. With this API, we can send emails on a local server as well as the live server.
How to use mail() in Laravel?
Step 1. Add Mail Configurations in .env file
MAIL_DRIVER = smtp
MAIL_HOST = smtp.gmail.com
MAIL_PORT = 587
MAIL_USERNAME = email
MAIL_PASSWORD = password
MAIL_ENCRYPTION = tls
Step 2. Create email templates
Laravel allows us to store email messages in our view files. For example, to manage our emails, we can create an email directory within our resources/views directory.
Step 3. Use mail() in controllers
public function sendEmail(Request $request, $id)
{
$user = Users::find($id);
Mail::send('emails.reminder', ['user' => $user], function ($mail) use ($user) {
$mail->from('[email protected]', 'Feedback');
$mail->to($user->email, $user->name)->subject('Thanks Message');
});
}
Laravel Auth is the process of identifying the user credentials with the database. Laravel managed it's with the help of sessions which take input parameters like username and password, for user identification. If the settings match then the user is said to be authenticated.
Auth is in-built functionality provided by Laravel; we have to configure.
We can add this functionality with php artisan make: auth
Auth is used to identifying the user credentials with the database.
- Offers a rich set of functionalities like Eloquent ORM, Template Engine, Artisan, Migration system for databases, etc
- Libraries & Modular
- It supports MVC Architecture
- Unit Testing
- Security
- Website built in Laravel is more scalable and secure.
- It includes namespaces and interfaces that help to organize all resources.
- Provides a clean API.
Developers use packages to add functionality to Laravel. Packages can be almost anything, from great workability with dates like Carbon or an entire BDD testing framework such as Behat. There are standalone packages that work with any PHP frameworks, and other specially interned packages which can be only used with Laravel. Packages can include controllers, views, configuration, and routes that can optimally enhance a Laravel application.
There are many packages are available nowadays also laravel has some official packages that are given below:-
- Cashier
- Dusk
- Envoy
- Passport
- Socialite
- Scout
- Telescope etc
Validation is the most important thing while designing an application. It validates the incoming data. It uses ValidatesRequests trait which provides a convenient method to authenticate incoming HTTP requests with powerful validation rules.
Here are some Available Validation Rules in Laravel are listed:-
- Alpha
- Image
- Date Format
- IP Address
- URL
- Numeric
- Size
- Min , Max
- Unique with database etc
With this @extends('layouts.master') we can extend this master layout in any view file.
In this example layouts are a folder that is placed in resources/views available and the master file will be there. Now "master.blade.php" is a layout file.
We can use
return redirect('/')->withErrors('You can type your message here');
return redirect('/')->with('variableName', 'You can type your message here');
return redirect('/')->route('PutRouteNameHere');
You can create a constants.php page in the config folder if does not exist. Now you can put a constant variable with value here and can use it with
Config::get('constants.VaribleName');
return [
'ADMINEMAIL' => '[email protected]',
];
Now we can display with
Config::get('constants.ADMINEMAIL');
You can do this in various ways. Steps are given below:-
- Copy .htaccess file from public folder and now paste it into your root.
- Now rename server.php file/page to index.php on your root folder.
- Now you can remove /public word from URL and refresh the page. Now it will work.
<script type="text/javascript">
$(document).ready(function() {
$("FORMIDORCLASS").submit(function(e){
// FORMIDORCLASS will your your form CLASS ot ID
e.preventDefault();
$.ajaxSetup({
headers: {
'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="_token"]').attr('content')
// you have to pass in between tag
}
})
var formData = $("FORMIDORCLASS").serialize();
$.ajax({
type: "POST",
url: "",
data : formData,
success: function( response ) {
// Write here your sucees message
}, error: function(response) {
// Write here your error message
},
});
return false;
});
});
</script>
Our first step should be
DB::connection()->enableQueryLog();
After our query, it should be placed
$querieslog = DB::getQueryLog();
After that, it should be placed
dd($querieslog)
DB::connection()->enableQueryLog();
$result = Blog:where(['status' => 1])->get();
$log = DB::getQueryLog();
dd($log);
request()->route()->getName()
php artisan make:model ModelNameEnter -mcr
$valiable1 = 'Best';
$valiable2 = 'Interview';
$valiable3 = 'Question';
return view('frontend.index', compact('valiable1', valiable2', valiable3'));
In you View File use can display by {{ $valiable1 }} or {{ $valiable2 }} or {{ $valiable3 }}
We have to call Facades in our controller file with this :
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Storage;
if($request->hasFile(file_name')) {
$file = Storage::putFile('YOUR FOLDER PATH', $request->file('file_name'));
}
We have to pass protected $table = 'YOUR TABLE NAME'; in your respective Model
namespace App;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Login extends Model
{
protected $table = 'admin';
static function logout() {
if(session()->flush() || session()->regenerate()) {
return true;
}
}
}
- Run this php artisan make:rule OlympicYear
- After that command it generates a file app/Rules/OlympicYear.php
- We can write rule in the passes() in OlympicYear.php generated file. It will return true or false depending on condition, which is this in our case
public function passes($attribute, $value)
{
return $value >= 1896 && $value <= date('Y') && $value % 4 == 0;
} - Next, we can update error message to be this:
public function message()
{
return ':attribute should be a year of Olympic Games';
} - Finally, we use this class in controller's store() method we have this code:
public function store(Request $request)
{
$this->validate($request, ['year' => new OlympicYear]);
}
For this you have to get value & assign value in controller file in __construct() like this.
public function __construct() {
$this->middleware(function ($request, $next) {
$name = session()->get('businessinfo.name'); // get value from session
View::share('user_name', $name); // set value for all View
View::share('user_email', session()->get('businessinfo.email'));
return $next($request);
});
}
1. Retrieving Data from session
session()->get('key');
2. Retrieving All session data
session()->all();
3. Remove data from session
session()->forget('key'); or session()->flush();
4. Storing Data in session
session()->put('key', 'value');
Soft delete is a laravel feature that helps When models are soft deleted, they are not actually removed from our database. Instead, a deleted_at timestamp is set on the record. To enable soft deletes for a model, we have to specify the soft delete property on the model like this.
In model we have to use namespace use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\SoftDeletes;
and we can use this
use SoftDeletes; in our model property.
After that when we will use delete() query then records will not remove from our database. then a deleted_at timestamp is set on the record.
Queues in Laravel are used by developers to create smooth application cycle by stacking complex tasks as jobs and dispatching these heavy jobs only with user permission or when it doesn’t disrupt the user experience.
We can add multiple AND operator at in a single where() conditions as well as we can also add separate where() for particular AND condition.
DB::table('client')->where('status', '=', 1)->where('name', '=', 'bestinterviewquestion.com')->get();
DB::table('client')->where(['status' => 1, 'name' => 'bestinterviewquestion.com'])->get();
Laravel supports various joins that's are given below:-
- Inner Join
DB::table('admin') ->join('contacts', 'admin.id', '=', 'contacts.user_id') ->join('orders', 'admin.id', '=', 'orders.user_id') ->select('users.id', 'contacts.phone', 'orders.price') ->get(); - Left Join / Right Join
$users = DB::table('admin') ->leftJoin('posts', 'admin.id', '=', 'posts.admin_id') ->get();
$users = DB::table('admin') ->rightJoin('posts', 'admin.id', '=', 'posts.admin_id') ->get(); - Cross Join
$user = DB::table('sizes') ->crossJoin('colours') ->get(); - Advanced Join
DB::table('admin') ->join('contacts', function ($join) { $join->on('admin.id', '=', 'contacts.admin_id')->orOn(...); }) ->get(); - Sub-Query Joins
$admin = DB::table('admin') ->joinSub($latestPosts, 'latest_posts', function ($join) { $join->on('admin.id', '=', 'latest_posts.admin_id'); })->get();
You can use request()->ip();
You can also use : Request::ip() but in this case, we have to call namespace like this: Use Illuminate\Http\Request;
request()->route()->getActionMethod()
Laravel involves Eloquent ORM (Object Relational Mapper), which makes it fun to interact with the database. While using Eloquent, every database table contains their corresponding “Model” that is being used for interaction with that table. The eloquent model also allows the people to insert, update, and delete the records from the table. We can create Eloquent models using the make:model command.
It has many types of relationships.
- One To One relationships
- One To Many relationships
- Many To Many relationships
- Has Many Through relationships
- Polymorphic relationships
- Many To Many Polymorphic relationships
Blade is very simple and powerful templating engine that is provided with Laravel. Laravel uses "Blade Template Engine".
1. How to set Cookie
To set cookie value, we have to use Cookie::put('key', 'value');
2. How to get Cookie
To get cookie Value we have to use Cookie::get('key');
3. How to delete or remove Cookie
To remove cookie Value we have to use Cookie::forget('key')
4. How to check Cookie
To Check cookie is exists or not, we have to use Cache::has('key')
We have to use the following artisan commands to enable/disable maintenance mode in Laravel 5.
Enable maintenance mode
php artisan down
Disable maintenance mode
php artisan up
It is a helper function which is used to dump a variable's contents to the browser and stop the further script execution. It stands for Dump and Die.
dd($array);
It is an array which contains all those fields of table which can be create directly new record in your Database table.
class User extends Model {
protected $fillable = ['username', 'password', 'phone'];
}
It is the reverse of fillable. When a guarded specifies which fields are not mass assignable.
class User extends Model {
protected $guarded = ['user_type'];
}
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Auth;
$userinfo = Auth::user();
print_r($userinfo );
Yes, It supports caching like Memcached and Redis. By default, laravel is configured with file cache which is stores the serialized, cached objects in the files. Normally we can use Memcached or Redis for large projects.
In Laravel, {{ $username }} and {!! $username !!} displays dynamic content within a Blade template. However, they have different behaviors depending on the context in which they are used.
{{ $username }} is used to display escaped output. This means that any special characters in the variable's value, such as HTML tags or JavaScript code, will be converted to their corresponding HTML entities to prevent them from being interpreted as code. This is done to help prevent cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks, where malicious code is injected into a web page.
{!! $username !!} is used to display unescaped output. This means the variable's value will be displayed exactly as it is, without any special characters being converted to HTML entities. This is useful when displaying HTML markup or other special characters.
However, using unescaped output can be risky, especially if the variable's value comes from user input. It can make your application vulnerable to XSS attacks. Therefore, you should always sanitize user input before displaying it on a web page and use the escaped output ({{ $variable }}) by default unless you have a good reason to use the unescaped output ({!! $variable !!}).
Laravel accessors and mutators are customs, user-defined methods that allow you to format Eloquent attributes. Accessors are used to format attributes when you retrieve them from the database.
1. Defining an accessor
The syntax of an accessor is where getNameAttribute() Name is capitalized attribute you want to access.
public function getNameAttribute($value)
{
return ucfirst($value);
}
2. Defining a mutator
Mutators format the attributes before saving them to the database.
The syntax of a mutator function is where setNameAttribute() Name is a camel-cased column you want to access. So, once again, let’s use our Name column, but this time we want to make a change before saving it to the database:
public function setNameAttribute($value)
{
$this->attributes['name'] = ucfirst($value);
}
Please update 'default' => env('DB_CONNECTION', 'mysql'), in config/database.php. Update MySQL as a database whatever you want.
In Laravel, dependency injection is a term used for the activity of injecting components into the user application. It’s a key element of agile architecture. The Laravel service container is a powerful tool that manages all class dependencies and performs dependency injection.
public function __construct(UserRepository $data)
{
$this->userdata = $data;
}
In this given an example, the UserController needs to retrieve users data from a data source(database). So, we can inject a service that is able to recover all users. In this example, our UserRepository most likely uses Eloquent to get user’s data from the database.
In Laravel, a closure is an anonymous function that often used as callback methods. Developers can also use it as a parameter in a function.
function handle(Closure $closure) {
$closure();
}
handle(function(){
echo ‘Best Interview Question’;
});We can start by adding a Closure parameter to the handle method. This will be used as type hint us that the handle method takes a Closure.
We can call the handle method and pass a service as a parameter.
By using
$closure();in the handle method we tell Laravel to execute the given Closure which will then display ‘Best Interview Question.’
We can create all web pages of our sites to tell Google and other search engines like Bing, Yahoo etc about the organization of our site content. These search engine web crawlers read this file to more intelligently crawl our sites.
Here are the steps that helps you to create real time sitemap.xml file and these steps also helps to create dynamic XML files.
- Firstly we have to create a route for this in your
routes/web.phpfile
Example
Route::get('sitemap.xml', 'SitemapController@index')->name('sitemapxml'); - Now you can create SitemapController.php with artisan command
php artisan make:controller SitemapController - Now you can put this code in your controller
public function index() {
$page = Page::where('status', '=', 1)->get();
return response()->view('sitemap_xml', ['page' => $page])->header('Content-Type', 'text/xml');
} - Now please create a view file in
resources/view/sitemap_xml.blade.phpfile with this code - Put this code in that created view file
<?php echo '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>'; ?>
<urlset xmlns="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9
http://www.sitemaps.org/schemas/sitemap/0.9/sitemap.xsd">
@foreach ($page as $post)
<url>
<loc>{{ url($post->page_slug) }}</loc>
<lastmod>{{ $post->updated_at->tz('UTC')->toAtomString() }}</lastmod>
<priority>0.9</priority>
</url>
@endforeach
</urlset>
- In Laravel, Queues are very useful for taking jobs, pieces of asynchronous work, and sending them to be performed by other processes and this is useful when making time-consuming API calls that we don’t want to make your users wait for before being served their next page.
- Another advantage of using queues is that you don’t want to work the lines on the same server as your application. If your jobs involve intensive computations, then you don’t want to take risk those jobs taking down or slowing your web server.
Please run below artisan commands step wise step.
php artisan config:clearphp artisan cache:clearcomposer dump-autoloadphp artisan view:clearphp artisan route:clear
There are sizable differences between laravel 4 and laravel 5 concerning LTS, features, file structures, etc.
Laravel four used to be the one who delivered large reputation to the Laravel framework, however this version no longer up to date anymore, and it also lacks a lot of functions released in Laravel 5.
- Laravel 4 released May 2013 however Laravel 5 released in February 2015.
- Laravel 5 has LTS Supports. It capability the LTS version stands for Long Term Support. It implies that bugfixes for that model will be provided for two years, till the next LTS version.
- A new listing app/Providers replaces the app/start archives from preceding versions of Laravel 4.x.
- Laravel 5 offers a Socialite bundle which is an optional, Laravel 5.0+ well matched package that provides painless authentication with OAuth providers.
- The favored dd helper function, which dumps variable debug information, has been upgraded to use the incredible Symfony VarDumper.
In distinction to Laravel four to 5 version differences, which is huge, 5.x and 5.y variations are now not that different. Some features added, some updated/removed in laravel 5, but the core structure stays the same.
Laravel Tinker is a powerful REPL tool which is used to interact with Laravel application with the command line in an interactive shell. Tinker came with the release of version 5.4 is extracted into a separate package.
How to install tinker
composer require laravel/tinker
How to execute
To execute tinker we can use php artisan tinker command.
- PHP version >= 7.2.0
- JSON PHP Extension
- BCMath PHP Extension
- Ctype PHP Extension
- Mbstring PHP Extension
- XML PHP Extension.
- Tokenizer PHP Extension
- OpenSSL PHP Extension
- PDO PHP Extension
Laravel offers a tool to include dummy data to the database automatically. This process is called seeding. Developers can add simply testing data to their database table using the database seeder. It is extremely useful as testing with various data types allows developers to detect bugs and optimize performance. We have to run the artisan command make:seeder to generate a seeder, which will be placed in the directory database/seeds as like all others.
How to create database seeder
To generate a seeder, run the make:seeder Artisan command. All seeders generated by the laravel will be placed in the database/seeds directory:
php artisan make:seeder AdminTableSeeder
With the help of update() function, we can update our data in the database according to the condition.
Blog::where(['id' => $id])->update([
'title' => ’Best Interview Questions’,
‘content’ => ’Best Interview Questions’
]);OR
DB::table("blogs")->where(['id' => $id])->update([
'title' => ’Best Interview Questions’,
‘content’ => ’Best Interview Questions’
]);
In case you are using save()
$blog = new Blog;
$blog->title = ‘Best Interview Questions’;
$blog->save()
// Now you can use (after save() function we can use like this)
$blog->id // It will display last inserted id
In case you are using insertGetId()
$insertGetId = DB::table(‘blogs’)->insertGetId([‘title’ => ‘Best Interview Questions’]);
Blog::where(['id' => 5])->orWhere([‘username’ => ‘[email protected]’])->update([
'title' => ‘Best Interview Questions’,
]);
Laravel provides a variety of aggregate functions such as max, min, count,avg, and sum. We can call any of these functions after constructing our query.
$users = DB::table(‘admin’)->count();
$maxComment = DB::table(‘blogs’)->max('comments');
Laravel provides various methods that we can use in queries to get records with our conditions.
These methods are given below
- where()
- orWhere()
- whereBetween()
- orWhereBetween()
- whereNotBetween()
- orWhereNotBetween()
- wherein()
- whereNotIn()
- orWhereIn()
- orWhereNotIn()
- whereNull()
- whereNotNull()
- orWhereNull()
- orWhereNotNull()
- whereDate()
- whereMonth()
- whereDay()
- whereYear()
- whereTime()
- whereColumn()
- orWhereColumn()
- whereExists()
We can use skip() and take() both methods to limit the number of results in the query. skip() is used to skip the number of results and take() is used to get the number of result from the query.
$posts = DB::table('blog')->skip(5)->take(10)->get();
// skip first 5 records
// get 10 records after 5
updateOrInsert() method is used to update an existing record in the database if matching the condition or create if no matching record exists.
Its return type is Boolean.
Syntax
DB::table(‘blogs’)->updateOrInsert([Conditions],[fields with value]);
DB::table(‘blogs’)->updateOrInsert(
['email' => '[email protected]', 'title' => 'Best Interview Questions'],
['content' => 'Test Content']
);
1. delete()
In case when we used to delete in Laravel then it removed records from the database table.
Example:
$delete = Post::where(‘id’, ‘=’, 1)->delete();
2. softDeletes()
To delete records permanently is not a good thing that’s why laravel used features are called SoftDelete. In this case, records did not remove from the table only delele_at value updated with current date and time.
Firstly we have to add a given code in our required model file.
use SoftDeletes;
protected $dates = ['deleted_at'];
After this, we can use both cases.
$softDelete = Post::where(‘id’, ‘=’, 1)->delete();
OR
$softDelete = Post::where(‘id’, ‘=’, 1)->softDeletes();
In Laravel, we can use whereBetween() function to get data between two dates.
Users::whereBetween('created_at', [$firstDate, $secondDate])->get();
How to create a Stored Procedure
To create a Stored Procedure you can execute given code in your MySQL query builder directly or use phpmyadmin for this.
DROP PROCEDURE IF EXISTS `get_subcategory_by_catid`;
delimiter ;;
CREATE PROCEDURE `get_subcategory_by_catid` (IN idx int)
BEGIN
SELECT id, parent_id, title, slug, created_at FROM category WHERE parent_id = idx AND status = 1 ORDER BY title;
END
;;
delimiter ;
After this, you can use this created procedure in your code in Laravel.
How to use stored procedure in Laravel
$getSubCategories = DB::select(
'CALL get_subcategory_by_catid('.$item->category_id.')'
);
We can use hasTable() to check table exists in our database or not.
Syntax
Schema::hasTable('users'); // here users are the table name.
if(Schema::hasTable('users')) {
// table is exists
} else {
// table is not exist
}
if(Schema::hasColumn('admin', 'username')) ; //check whether admin table has username column
{
// write your logic here
}
Inserts(): This method is used for insert records into the database table. No need the “id” should be autoincremented or not in the table.
Example
DB::table('bestinterviewquestion_users')->insert(
['title' => 'Best Interview Questions', 'email' => ‘[email protected]’]
);
It will return true or false.
insertGetId(): This method is also used for insert records into the database table. This method is used in the case when an id field of the table is auto incrementing.
It returns the id of current inserted records.
Example
$id = DB::table('bestinterviewquestion_users')->insert(
['title' => 'Best Interview Questions', 'email' => ‘[email protected]’]
);
Reverse routing in the laravel means the process that is used to generate the URLs which are based on the names or symbols. URLs are being generated based on their route declarations.
With the use of reverse routing, the application becomes more flexible and provides a better interface to the developer for writing cleaner codes in the View.
Route:: get(‘list’, ‘blog@list’);
{{ HTML::link_to_action('blog@list') }}
A Traits are a technique for code reuse in single inheritance languages.
I Created a Traits directory in my Http directory named BrandTrait.php
use App\Http\Traits\BrandTrait;
class YourController extends Controller {
use BrandTrait;
public function addProduct() {
//$brands = Brand::all();
// $brands = $this->BrandTrait(); // this is wrong
$brands = $this->brandsAll();
}
}Here is my BrandTrait.php
namespace App\Http\Traits;
use App\Brand;
trait BrandTrait {
public function brandsAll() {
// Get all the brands from the Brands model or table.
$brands = Brand::all();
return $brands;
}
}
You can use the following syntax to check ajax request in laravel.
if ($request->ajax()) {
// Now you can write your code here.
}
To check the email value is sent or not in request, you can use $request->has('email')
if($request->has('email')) {
// email value is sent from request
} else {
// email value not sent from request
}
Laravel includes a number of global "helper" string and array functions. These are given below:-
Laravel Array Helper functions
- Arr::add()
- Arr::has()
- Arr::last()
- Arr::only()
- Arr::pluck()
- Arr::prepend() etc
Laravel String Helper functions
- Str::after()
- Str::before()
- Str::camel()
- Str::contains()
- Str::endsWith()
- Str::containsAll() etc
Views contain the HTML provided by our application and separate our controller or application logic from our presentation logic. These are stored in the resources/views directory.
<html>
<body>
<h1>Best Interview Question<h1>
</body>
</html>
Faker is a type of module or packages which are used to create fake data for testing purposes. It can be used to produce all sorts of data.
It is used to generate the given data types.
- Lorem text
- Numbers
- Person i.e. titles, names, gender, etc.
- Addresses
- DateTime
- Phone numbers
- Internet i.e. domains, URLs, emails etc.
- Payments
- Colour, Files, Images
- UUID, Barcodes, etc
In Laravel, Faker is used basically for testing purposes.
REPL is a type of interactive shell that takes in single user inputs, process them, and returns the result to the client.
The full form of REPL is Read—Eval—Print—Loop
You can use php artisan key:generate to generate your application key.
Where Null Query
DB::table('users')->whereNull('name')->get();
Where Not Null Query
DB::table('users')->whereNotNull('name')->get();
ACL Stands for Access Control List.
If you needed to control get entry to certain sections of the site, or flip on or off unique portions of a web page for non-admins, or ensure any person can only edit their very own contacts, you wanted to deliver in a device like BeatSwitch Lock or hand-roll the functionality, which would be something referred to as ACL: Access Control Lists or basically the capability to outline a persons' capability to do and see certain matters primarily based on attributes of their person record.
Laravel 6.0 is incorporated with a number of latest features such as Laravel vapor compatibility, semantic visioning, job middleware, lazy collections, eloquent sub-query enhancements, Laravel users interface, etc. The Laravel 6.0 released on 3rd September 2019 with the latest and unique features.
Advanced Features of Laravel 6.0
- Laravel Vapor Compatibility
- Semantic Versioning
- Job Middleware
- Laravel User Interface (UI)
- Eloquent Subquery Enhancements
- Improved Authorization Responses
- Lazy Collections
In between head, tag put <meta name="csrf-token" content="{{ csrf_token() }}"> and in Ajax, we have to add
$.ajaxSetup({
headers: {
'X-CSRF-TOKEN': $('meta[name="csrf-token"]').attr('content')
}
});
Eager loading is used when we have to fetch some useful data along with the data which we want from the database. We can eager load in laravel using the load() and with() commands.
with() function is used to eager load in Laravel. Unless of using 2 or more separate queries to fetch data from the database, we can use it with() method after the first command. It provides a better user experience as we do not have to wait for a longer period of time in fetching data from the database.
You can use an artisan command php artisan --version to know the laravel version.
After running the composer install in the project directory, the composer will generate the composer.lock file.It will keep a record of all the dependencies and sub-dependencies which is being installed by the composer.json.
LTS Stands for Long Term Support. LTS variations get hold of bug fixes for two years, and protection fixes for three years. General minor releases handle bug fixes for six months and protection fixes for one year. Laravel 5.5 is the next long-time period support (LTS) version of Laravel.
You can extend the login expire time with config\session.php this file location. Just update lifetime the value of the variable. By default it is 'lifetime' => 120. According to your requirement update this variable.
'lifetime' => 180
You can cut out a route from CSRF verification by using adding the route to $except property at VerifyCsrfToken middleware.
protected $except = [
'admin/*/edit/*'
];
If we want to get a table in Laravel application from a particular Model then we can use getTable() method.
$user = new BestInterviewQuestions;
$tableName = $user->getTable();
print_r($tableName);
- Open the laravel project inside the code editor.
- Go to the Composer.json file and change the laravel/framework from 5 to 6.
- Open the terminal and write the command – composer update and hit enter to wait for the update to complete.
- After finished run the server command (PHP artisan serve) and run the project in a browser.
- After this , again go to terminal and write command –(composer require laravel/ui) and hit enter and download the packages.
- Then, for creating the auth file write the command ( PHP artisan ui vue-auth) to make the auth file in laravel 6.0.
In this way, we can upgrade from laravel 5 to laravel 6.
Laravel is believed to be a very adaptable application creation PHP framework. This is due in large part to the features of Laravel that include two-way binding of data as well as quick and easy transitions, unit testing integration with messaging applications, as well as many other features.
- Easy Installation
- Database Migration
- Supports MVC Architecture
- Traffic Management
- Robust Security Features
- Modular Design
- Object-Oriented Libraries
- Cloud Storage Option
- Host of Libraries
We can do it with 3 simple steps.
- Press Ctrl + Shift + ESC. Locate the php system walking artisan and kill it with proper click -> kill process.
- Reopen the command-line and begin again the server.
- Note that you ought to be able to kill the manner just by using sending it a kill sign with Ctrl + C.
Here is an example to understand the concept of using group_concat() to join in Laravel. We have 3 tables like "dynamic_forms", "dynamic_forms_mapping", "categories".
$list = DB::table('dynamic_forms')
->select("dynamic_forms.*" ,DB::raw("(GROUP_CONCAT(wf_categories.name SEPARATOR ', ')) as category"))
->leftjoin("dynamic_forms_mapping", "dynamic_forms_mapping.form_id","=","dynamic_forms.id")
->leftjoin("categories", "dynamic_forms_mapping.category_id","=","categories.id")
->groupBy('dynamic_forms.id')
->where('dynamic_forms.status', 1)
->get();
All the service providers get registered in the configuration file known as config/app.php. This is the file that contains the provider's array and here the user is able to list all the class names for the respective service providers. And by default, the set of service providers of Laravel core are listed inside this array. Now, these services providers bootstrap all the Laravel components that are core, like the mailer, cache, queue, and others. So, to register a required provider, add that provider to the array:
'providers' => [
// Other Service Providers
App\Providers\ComposerServiceProvider::class,
],
ORM Stands for Object Relational Mapping.
It allows us to easily define a single route to handle all activities in a controller. We can define the route using the Route::controller method:
Listeners handle each and every activity that is mentioned in the event being registered. An artisan command which is event: generate creates all of the listeners inside the app/listeners directory. This Listeners folder holds a file namely “EventListener.php “ that has every single method required to handle listeners.
EventListener.php
namespace App\Listeners;
use App\Events\SomeEvent;
use Illuminate\Queue\InteractsWithQueue;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue;
class EventListener{
public function __construct() {
//
}
public function handle(SomeEvent $event) {
//
}
}As mentioned above in this code, it involves the handle function to manage various events. Also, we can build several independent listeners which will target one single event.
Laravel Gate holds a sophisticated mechanism that ensures the users that they are authorized for performing actions on the resources. The implementation of the models is not defined by Gate. This renders the users the freedom of writing each and every complex spec of the use case that a user has in any way he/she wishes. Moreover, the ACL packages can be used as well with the Laravel Gate. With the help of Gate, users are able to decouple access logic and business logic. This way clutter can be removed from the controllers.
You can use php artisan migrate:rollback --step=1.
Forge in Laravel is one tool that is used for deploying as well as configuring numerous web applications. This was created by the developers of the renowned Laravel framework, though this can be utilized for automating the deployment-related to any of the web application on the condition that these applications use the PHP server. Forge in Laravel automates each and every necessary installation as well as configuration step, which enables users to get their website up along with running quickly.
Laravel is an appropriate choice for PHP builders to use for building an API, especially when a project’s necessities are not exactly defined. It's a comprehensive framework suitable for any type of application development, is logically structured, and enjoys robust community support.
Laravel includes factors for not solely API development, but front-end templating and singe-page software work, and other aspects that are totally unrelated to only building a net utility that responds to REST Http calls with JSON.
We use events and listeners in the laravel because events give the basic observer implementation that allows any user to subscribe and listen to multiple events that are triggered in the web application. Every listeners are stored in the app/Listeners folder and event class in the laravel is stored in the app/Events folder .
Pusher is one hosted service with the help of which it has become immensely easy to add data of real-time along with functionality to the web as well as mobile applications. Laravel Pusher sits like one real-time layer among the servers and the clients. It manages persistent connections with the clients. Plus it also offers libraries for integration into all of the major runtimes as well as frameworks. PHP, Python, Ruby, Java, Node as well as Go on the servers plus JavaScript, Java (Android) on the clients and Objective-C (iOS).
The Laravel 5.1 framework comprises functionality named broadcasting events. This new functionality makes it quite easy to build real-time applications in PHP. And with this, an app will be able to publish the events to a number of real-time cloud-based PubSub solutions, such as Pusher, or Redis. Also, with this functionality called the broadcasting events which is built into the Laravel 5.1, it now became easier creating real-time applications for the PHP developers. This latest real-time capability unbars numerous possibilities that were available only to applications written for the other platforms such as Node.js.
The echo in Laravel is one tool due to which it is easy for the users to bring in the Websocket's power to their Laravel applications. Echo streamlines some of the most common as well as the most complex aspects of making complicated WebSockets interactions. It comes in two parts, one- the series of amendments to the Event broadcasting system of Laravel and two- the new package of JavaScript.
Horizon in Laravel is the queue manager. It provides the user with full control of the queues, it renders the means for configuring how the jobs are processed and generates analytics, plus performs various tasks related to queue from within one nice dashboard.
Dusk in Laravel renders one expressive and easy-to-use type of browser automation along with testing API. This By default does not demand to install the JDK or Selenium on the device. Instead, it uses one standalone installation of ChromeDriver. However, the users are free for utilizing any of the other compatible drivers of Selenium as per their wishes.
Mix in Laravel renders one fluent API to define Webpack creation steps for the application of Laravel that uses various common CSS as well as JavaScript preprocessors. With the help of one easy method of chaining, the user is able to fluently define the asset pipeline.
mix.js('resources/js/app.js', 'public/js') // You can also use your custom folder here
.sass('resources/sass/app.scss', 'public/css');
Gulp in Laravel is simply one implementation that targets to make it comfortable for the users who have recently acquainted themselves with the gulp in Laravel to be capable to manage their gulp file through adding the modules that work efficiently.
Vapor in Laravel is a serverless deployment platform auto-scaling and powered by AWS Lambda. It used to manage Laravel Infrastructure with the scalability and simplicity of serverless.
The Singleton Design Pattern in Laravel is one where a class presents a single instance of itself. It is used to restrict the instantiation of a class to a single object. This is useful when only one instance is required across the system. When used properly, the first call shall instantiate the object and after that, all calls shall be returned to the same instantiated object.
It allows using objects without having to know how these objects are persisted. It is an abstraction of the data layer. It means that our business logic no need to know how data is retrieved. The business logic relies on the repository to get the correct data.
Basically it is used to decouple the data access layers and business logic in our application.
Laravel contracts are a special set of interfaces used among multiple functionalities and other core services that are within the framework.
Design patterns are not prepared instructions or libraries, that can be definitely utilized to your system, this is no longer a concrete solution that can be converted into source code, plan patterns are an awful lot greater than that. They are patterns or templates, that can be carried out to resolve a problem in different particular situations.
Design Patterns in Laravel
- The Builder pattern
- The Repository pattern
- The need for the Builder pattern
- The need for the Factory pattern
- The Factory pattern
- The Provider pattern
- The Facade pattern
- The Strategy pattern
- The need for the Repository pattern etc
In Laravel, Authorization is a process in which the system or web application verifies whether authenticated users can access the resources requested. Basically, it checks and verifies rights and permissions over a particular resource before giving authorization to the user.
If you want to rollback a specific migration, look in your migrations table, you’ll see each migration table has its own batch number. So, when you roll back, each migration that was part of the last batch gets rolled back.
Use this command to rollback the last batch of migration
php artisan migrate:rollback --step=1
Now, suppose you only want to roll back the very last migration, just increment the batch number by one. Then next time you run the rollback command, it’ll only roll back that one migration as it is a batch of its own.
Here are some of the reasons why Laravel is considered to be better than CodeIgniter:
| Laravel | CodeIgniter |
|---|---|
| It supports Eloquent object-relational mapping ORM. | It does not support ORM. |
| It has in-built modularity features. | It requires users to create and maintain modules using Modular Extension. |
| It is straightforward to perform Database Schema Migration. | There are no particular features to simplify Database Schema Migration. |
| It provides an in-built template engine, called Blade. | It does not provide an in-built template engine. |
| It is easier to develop REST API. | Developing REST API is complicated. |
| Allows developers to establish custom HTTP Routes. | It does not support HTTP Routes completely. |
NOTE: If you are looking CodeIgniter Questions for interview preparations, then you can visit here.
You can run this Artisan Command php artisan queue:work --tries=3 OR --once --queue=JobQueueName
You can use both --tries or --once. When you will use --once then you command will execute singly and when you will use --tries=2 the it will execute two times and further.
Laravel 8.0 is incorporated with a number of latest features such as Laravel Jetstream, model directory, migration squashing, rate limiting improvements, model factory classes, time testing helpers, dynamic blade components and, much more. The Laravel 8.0 released on 8th September 2020 with the latest and unique features.
New Features in Laravel 8
- Time Testing Helpers
- Models Directory
- Migration Squashing
- Laravel Jetstream
- Rate Limiting Improvements
- Model Factory Classes
- Dynamic Blade Components
Yes, Laravel supports caching of popular backends such as Memcached and Redis.
To run test cases in Laravel, you should use the PHPUnit or artisan test command.
namespace Tests\Unit;
use PHPUnit\Framework\TestCase;
class ExampleTest extends TestCase
{
* @return void
public function testBasicTest()
{
$this->assertTrue(true);
}
}
The Eloquent cursor () method allows a user to iterate through the database records using a cursor, which will execute only a single query. This method is quite useful when processing large amounts of data to significantly reduce memory usage.
Follow these steps to successfully create a package in Laravel:
- Creating a Folder Structure
- Creating the Composer File
- Loading the Package from the Main Composer.JSON File
- Creating a Service Provider for Package
- Creating the Migration
- Creating the Model for the Table
- Creating a Controller
- Creating a Routes File
- Creating the Views
- Updating the Service Provider to Load the Package
- Update the Composer File
In Laravel, Facades are used to provide a static interface to classes available inside the application's service container.
Now, unlike conventional static method calls, facades can be mocked in Laravel. It can be done using the shouldRecieve method, which shall return an instance of a facade mock.
$value = Cache::get('key');
Cache::shouldReceive('get')->once()->with('key')->andReturn('value');
In laravel, we can call multiple Middlewares in Controller file and route file.
1. In Controller file, you can call like this.
public function __construct() {
$this->middleware(['revalidateBackHistory', 'validateUser']);
}
2. In route file, you can call multiple middleware like this.
Route::get('/', function () {
//
})->middleware(['firstMiddle', 'secondMiddle']);
Normal HTML forms do not support the PUT, PATCH, or DELETE actions. That's why while defining the PUT, PATCH or DELETE routes which are being called from an HTML form, you will have to add a hidden _method field to the form.
The value which is sent with the _method field will get used as the HTTP request method, like this:
<form action="/foo/bar" method="POST">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="PUT">
<input type="hidden" name="_token" value="{{ csrf_token() }}">
</form>
To generate the _method input, you can use the @method Blade Directive, like this:
<form action="/foo/bar" method="POST">
@method('PUT')
@csrf
</form>
This is called method spoofing in Laravel.
To use multiple databases in Laravel, follow these steps carefully.
- Ensure these settings in the .env file
- Add these following lines of code in the config/database.php file to clearly define the relationship between the two databases
- Execute the query with particular database.
1. Ensure these settings in the .env file
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=localhost
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=your_db_name
DB_USERNAME=bestinterviewquestion
DB_PASSWORD=admin@123
DB_CONNECTION_SECOND=mysql
DB_HOST_SECOND=localhost
DB_PORT_SECOND=3306
DB_DATABASE_SECOND=your_db_name2
DB_USERNAME_SECOND=bestinterviewquestion
DB_PASSWORD_SECOND=admin@12345
2. Add these following lines of code in the config/database.php file to clearly define the relationship between the two databases
'mysql' => [
'driver' => env('DB_CONNECTION'),
'host' => env('DB_HOST'),
'port' => env('DB_PORT'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE'),
'username' => env('DB_USERNAME'),
'password' => env('DB_PASSWORD'),
],
'mysql2' => [
'driver' => env('DB_CONNECTION_SECOND'),
'host' => env('DB_HOST_SECOND'),
'port' => env('DB_PORT_SECOND'),
'database' => env('DB_DATABASE_SECOND'),
'username' => env('DB_USERNAME_SECOND'),
'password' => env('DB_PASSWORD_SECOND'),
],
3. Execute Query
$users = DB::connection('your_db_name2')->select();
Laravel 9 is now available. It comes with a variety of new features. These include an improved accessor/mutator API and better support for Enum cast, forced scope bindings, and a new database engine to power Laravel Scout.
New Features in Laravel 9
- Minimum PHP Requirement
- Anonymous Stub Migration
- Controller Route Groups
- Forced Scoping Of Route Bindings
- Implicit Route Bindings With Enums
- Improved Eloquent Accessors / Mutators
- Bootstrap 5 Pagination Views
- New Interface for the Query Builder
- Symfony Mailer & Flysystem 3.x
- Slot Name Shortcut
- Full Text Indexes / Where Clauses
- Rendering Inline Blade Templates
- Improved Validation Of Nested Array Data
- Test Coverage Using Artisan test Command etc.
For more info, you can visit here.
Laravel is a popular open-source PHP web application framework that follows the MVC architectural pattern. It was created by Taylor Otwell in 2011 and has gained a large and active community of developers.
Laravel is known for its elegant syntax, robust features, and developer-friendly approach. It offers a wide range of features out of the box, including routing, middleware, authentication, templating, and database migration tools. Additionally, Laravel has a modular structure that allows developers to pick and choose the components they need for their specific project, making it highly customizable. One of the key features of Laravel is its object-relational mapping (ORM) system, which makes it easy to work with databases by allowing developers to interact with database tables using PHP classes. Laravel's ORM, called Eloquent, simplifies creating, retrieving, updating, and deleting records from a database.
Another unique feature of Laravel is its built-in support for unit testing and integration testing, making it easy to ensure that your code functions correctly and that new features or changes do not break existing functionality. Compared to other PHP frameworks, Laravel is often praised for its clean and expressive syntax, which makes it easier for developers to write and read code. Laravel also strongly focuses on developer experience, offering a powerful command-line interface (CLI) called Artisan, which provides many helpful tools for managing a Laravel application.
Overall, Laravel's elegant syntax, robust features, and developer-friendly approach make it a popular choice for building web applications in PHP.
Composer is a dependency manager for PHP widely used in the PHP community, including the Laravel framework. Composer allows developers to declare the libraries and packages their projects depend on, and it manages the installation and updating of those dependencies.
- The importance of Composer in Laravel is significant because Laravel itself and most of its third-party packages rely on Composer for installation and management.
- Composer simplifies installing and updating dependencies, reducing the time and effort required to manage a Laravel project's dependencies.
- Composer manages dependencies for the framework itself and any packages or libraries that a developer may use in their Laravel project.
- The composer.json file is used to declare dependencies and the composer.lock file is generated to ensure that everyone working on the project uses the same dependencies versions.
The composer plays a crucial role in the Laravel ecosystem by simplifying dependency management, reducing the risk of version conflicts, and streamlining the development process.
Laravel, a popular PHP web application framework, provides a built-in queueing system that allows developers to defer the processing of time-consuming tasks, such as sending emails or processing large amounts of data, to a later time.
Here's a brief overview of how Laravel implements queueing and job scheduling:
- Laravel uses different queue drivers, such as Redis, Beanstalkd, Amazon SQS, and databases, to manage the queue of jobs. Each driver provides a different implementation, but they all follow the same basic principle of pushing jobs into a queue and popping them off when they're ready to be processed.
- To create a job in Laravel, use the make: job Artisan command or create a new class that extends the Illuminate\Queue\Jobs\Job class. A job class typically defines a handle() method that contains the logic to be executed when the job is processed.
- Once a job is created, it can be dispatched to the queue using the dispatch() or dispatchNow() methods. The former method puts the job onto the queue, while the latter method executes the job immediately without queueing it.
- Laravel provides a simple interface for scheduling jobs using the Illuminate\Console\Scheduling\Schedule class. You can define a schedule by chaining methods to specify when a job should run, such as daily() or hourly(), and then use the run() method to specify the job to be executed.
- Laravel also provides a convenient way to monitor the status of jobs and queues using the php artisan queue: work command, which starts a worker process that listens for new jobs and processes them as they become available. You can also use the php artisan queue: failed command to view and manage failed jobs.
Overall, Laravel's queueing system is a powerful and flexible way to handle time-consuming tasks in a web application. Its simple interface makes it easy to use and customize for your needs.
It is one of the most frequently asked questions in Laravel advanced interview questions. So, prepare yourself! The answer to this is Laravel 10 is the latest version of Laravel and was released on February 14, 2023.
Some key new features of Laravel 10 include Native PHP types, Laravel Pennant, a new process abstraction layer, and improved security. Other features include routing, caching, authentication, database migration, ORM (Eloquent), Blade templating engine, queue management, and artisan command-line interface. Laravel's new features enhance web application performance, security, and functionality.
This is another important question in Laravel interview questions for 5 years of experience. Laravel uses the Model-View-Controller (MVC) pattern, a core architectural pattern. Within Laravel, the MVC pattern is crucial in organizing code and separating distinct aspects of application logic. This separation enhances manageability and maintainability.
- Model: The Model component represents the data and encompasses its business logic.
- View: The View component presents the user interface that enables interaction with the data.
- Controller: The Controller component handles user requests, interacts with the Model to perform required actions or retrieve data, and ultimately renders the appropriate View to visualize and interact with.
By applying the MVC pattern, Laravel ensures a clear distinction between these three components, promoting a more structured and scalable development approach.
Laravel 10 supports a variety of databases, allowing developers to choose the one that best suits their project requirements. The databases supported by Laravel 10 include MySQL, PostgreSQL, MariaDB 10.3+ (Version Policy), SQLite and SQL Server.
Laravel's database layer is designed to utilize the PDO (PHP Data Objects) library, allowing it to seamlessly integrate with a wide range of databases supported by PDO. This flexibility enables developers to connect Laravel with other databases, such as Oracle, IBM DB2, etc., by configuring the database connection settings accordingly.
The "env" file in Laravel is a central configuration file that allows developers to define and manage environment-specific settings for their applications. It provides flexibility and adaptability to your Laravel project across different environments, like local development, staging, and production. You can store sensitive information like database credentials, API keys, and other settings in an "env" file. You can access these variables using the env helper or the Config facade.
Simply put, the "env" file in Laravel provides a flexible and secure method to manage environment-specific configurations by defining variables. Moreover, configuration enhances your application's security and promotes collaboration among team members by providing a centralized location to manage and share configuration settings.